Physicians as well as scientists have produced a variety of tools to assist them to evaluate the outcome of almost all health problems and use them to help assess the impact of their health condition on the particular person. These are utilized in clinical practice to measure improvement in therapy and utilized in research to determine improvements coming from treatment options that are being researched.
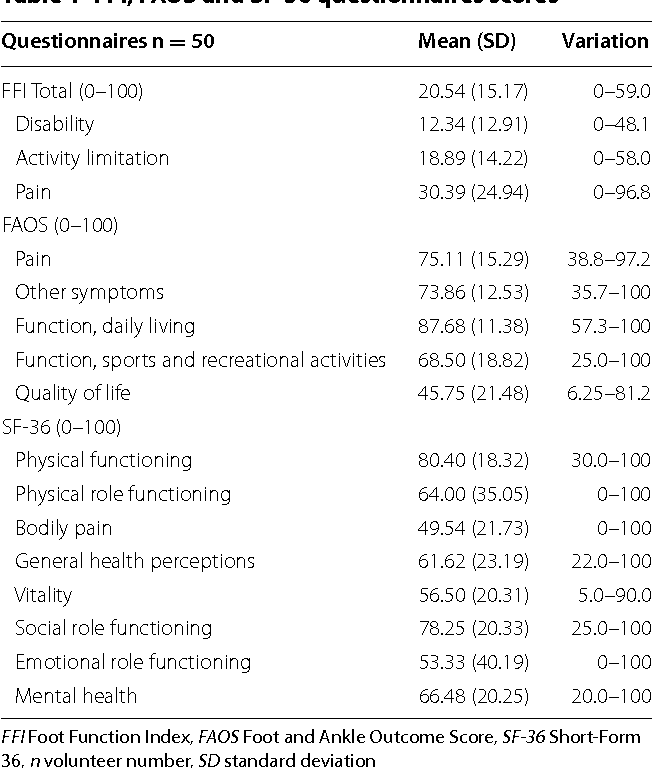
The Foot Function Index (FFI) was created in 1991 as a resource for clinicians and researchers to determine the effect of foot conditions on function when it comes to discomfort, impairment as well as activity limitation of the people with the issue. It’s a survey like tool that consisted of 23 questions. The FF I was originally created in the context with the problems with the feet that happen in rheumatoid arthritis, but it has become widespread in clinical and research settings for a wide range of foot conditions. The Foot Function Index set of questions has 23 questions that are separated into three subcategories based on patient values in the 3 domains of pain, impairment and activity limitation. The affected person completes the questionnaire to score each question on the range from 0 (pain free or no difficulty) to 10 (worst pain imaginable or so hard it needs help), which best represents their foot within the previous week. The general score provides the Foot Function Index and there are additionally a score for each of the 3 sub-scales.
Of worry with all of these types of applications that measure outcomes and associated issues is always that is the instrument dependable and is it valid? Various research projects about the test-retest repeatability of the Foot Function Index complete and also sub-scale ratings have been reported with the statistics being from 0.87 to 0.69 and that is regarded as adequate. It’s been subjected to testing mainly on individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and the summary of this research is that it is a dependable tool to work with in these patients. Robustness of any questionnaire type application is recognized as extremely important and is a way of testing if the application is repeatable, in that it provides as close as you possibly can to the similar outcome should it be used again. Equally as necessary as repeatability is the approach which the FFI is correct. Validity identifies if the instrument is measuring what it actually claims that it is measuring. One study which looked at this for the FFI revealed a strong relationship between the FFI total and sub-scale rankings and other clinical measures of foot signs and symptoms that confirms that there is very good criterion validity of the Foot Function Index. Another necessary feature of instruments such as this is that they would be the responsive. This will mean that if the tool is needed again after a period of time and there has been a change in the signs and symptoms, is the tool sensitive enough and responsive enough to pick up that alteration. The FFI has become ranked positively for responsiveness.
Since the first development a adjusted version of the FFI has been created to change the features of the application to allow it to be more consistent with WHO guidelines. Many experts have translated this FFI into a number of different languages where it’s just as before been evaluated if it is dependable and appropriate in those languages. Most of the research thus far indicates that it is valid and reliable.
Advertisement:
- Hardcover Book
- Uchida, Thomas K. (Author)
- Hardcover Book
- Merton Root, William Phillip Orien and John Weed (Author)
I get commissions for purchases made through links on this website. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.



